Hot chamber die casting and cold chamber die casting are two types of die casting processes that differ in the method used to inject molten metal into the die.
What is Hot Chamber Die Casting and How Does It Work?
In hot chamber die casting, the molten metal is contained in a pool within the machine and is fed into the die through a gooseneck and piston.
This process is suitable for metals with low melting temperatures such as zinc and magnesium.
The hot chamber process cannot accommodate alloys with high melting temperatures, as it will result in damage to the gooseneck, nozzle, and other components of the casting machine.
How Does It Work?
Hot-chamber die casting machines rely upon a pool of molten metal to feed the die. At the beginning of the cycle, the piston of the machine is retracted, which allows the molten metal to fill the “gooseneck”.
The pneumatic- or hydraulic-powered piston then forces this metal out of the gooseneck into the die.
Pros:
- Faster cycle times: Since the molten metal is already contained within the machine, hot chamber die casting can have faster cycle times compared to cold chamber die casting.
- Less turbulence: The gooseneck and piston mechanism used in hot chamber die casting can result in less turbulence when injecting the molten metal into the die. This can lead to better surface finish and dimensional accuracy of the final product.
- Suitable for low melting point alloys: Hot chamber die casting is suitable for alloys with low melting temperatures such as zinc and magnesium.
- Automated production: Hot chamber die casting machines can be fully automated, allowing for high volume production with minimal labor costs.
- More precise dimensional workpieces can be made: Because liquid zinc alloy has good fluidity, high-precision dimensional products can be produced in one go, eliminating the tedious post-processing process and reducing overall production costs.
Cons:
- Limited material options: Hot chamber die casting is only suitable for alloys with low melting temperatures such as zinc and magnesium.
- Not suitable for large parts: Hot chamber die casting is not well-suited for producing large parts
Cannot accommodate alloys with high melting temperatures as it will result in damage to the gooseneck, nozzle, and other components of the casting machine.
What is Cold Chamber Die Casting and How Does It Work?
Cold chamber die casting involves pouring molten metal into a separate chamber before it is injected into the die through a hydraulic or mechanical piston. This process is suitable for metals with higher melting temperatures such as aluminum and copper alloys.
How Does It Work?
In cold chamber die casting, the molten metal is first melted in a separate furnace and then ladled or poured into the injection chamber of the machine. The injection chamber is not heated and is kept at a lower temperature than the molten metal.
Once the molten metal is in the injection chamber, a hydraulic or mechanical piston is used to force it into the die. The high pressure used during this process ensures that the molten metal fills all of the details of the die and produces a high-quality cast part.
Pros:
- Strong and long-lasting components: Cold chamber die casting helps to create parts that are strong and long-lasting.
- Increased strength: The high pressure used during the injection process in cold chamber die casting can result in increased strength of the final product.
- Easy assembly: Parts produced through cold chamber die casting can be designed with features that make assembly easier.
Cons:
- Slower production cycles: Cold chamber die casting can have slower production cycles compared to hot chamber die casting.
- Difficulty casting low-fluidity metals: It can be difficult to cast low-fluidity metals using cold chamber die casting. It‘s also difficult to produce precise dimensions and post-processing is needed to achieve dimensional requirements
- Porosity: Most casting processes, including cold chamber die casting, can result in a small amount of porosity in the finished parts.
Differences between hot and cold chamber
The main difference between these two processes lies in how the molten metal is fed into the die. Hot chamber machines have a built-in pool of molten metal while cold chamber machines require an external source of molten metal.
Which Type of Die Casting Is Best for Your Project?
Both processes have their own unique advantages and disadvantages.
The best type of die casting for your project depends on several factors:
- Material being cast
- Size and complexity of the part
- Production requirements
- Cost considerations
Complete zinc die-casting solution with our services and machinery
TAZIMAC One-stop services
We have a professional team to help you complete the one-stop service requirements from procurement to delivery to serve new customers and foreign customers. You can easily choose equipment, and will not waste extra money on the unnecessary option.
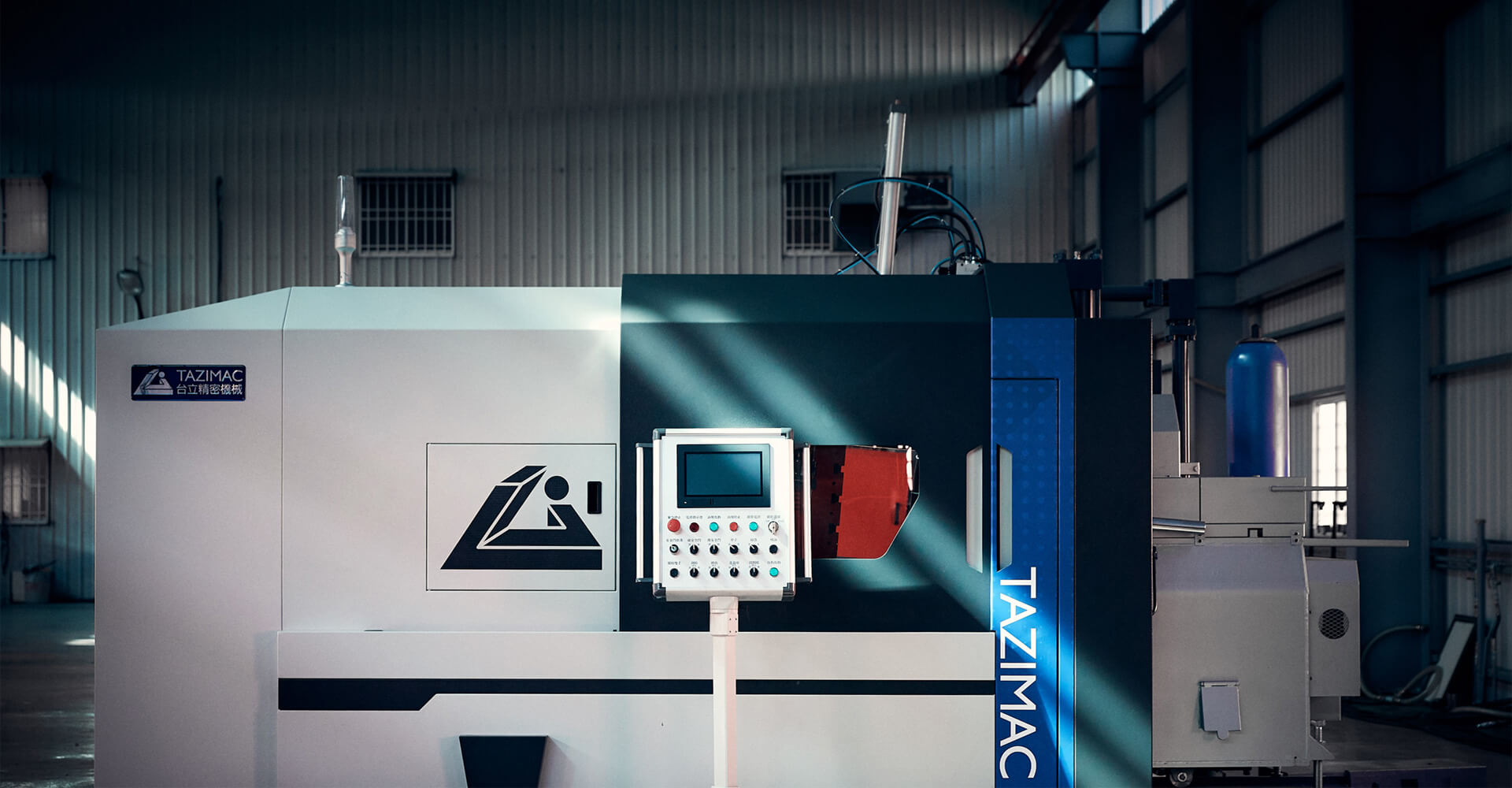

Zinc Hot Chamber Die Casting Machine
TAZIMAC develops many automation peripherals related to zinc alloy equipment with a focus on integrating the entire series of peripherals.
In addition to assisting users in efficient production, the peripherals are easy to maintain and troubleshoot due to their high software and hardware compatibility resulting from self-development and integration.
Learn about how this innovative equipment to reduce your carbon footprint and save electricity in the process:
INNOVATIONS IN ZINC HOT CHAMBER DIE CASTING EQUIPMENT THAT REDUCE CARBON FOOTPRINT